LNG market in Q2 2025
Summary of events in Q2 2025
Geopolitics became leitmotif of global LNG market in the second quarter. This quarter is usually quite boring due to high predictability of the market’s fundamentals. But it not the case this time.
In April, Trump imposed high so-called “reciprocal“ import duties on almost all US trading partners. Since then, Trump has changed and keeps changing his approach to duties, but it was this event that became key factor of uncertainty about future trade flows on international energy markets. Fluctuations in spot LNG prices at time of announcements exceeded 10%. Trump administration is forcing countries to purchase namely US LNG, as well as to invest in future US LNG projects (primarily the Alaska LNG plant).
Joint Israeli and US on Iran, which lasted from June 13 to 24, also led to serious turmoil in the spot market. Provision by Qatar and the UAE of its territory to for US military forces for direct attack of Iran has reasonably caused expectations of retaliation. Changing estimation of geopolitical premium in spot LNG prices led to sharp jumps in JKM price.
As of 30.06.2025, there were 47 LNG plants in the world with a total LNG liquefaction capacity of 485 MTPA. 11 plants were fully or partially idle with total non-operational capacity of 42 MTPA.
In 2025, 49.5 MTPA of LNG capacity is expected to be commissioned. It is close to record amount of 51.8 MTPA back in 2009. However, next year record could be broaken - 57.9 MTPA is going to be commissioned in 2026. USA dominates LNG build up: 62% of new capacity in 2025 and 43% in 2026 will be commissioned in USA (plus US project in Mexico).
Venture Global LNG, founded by financier Michail Sabel, formally commissioned Calcasieu Pass LNG plant in Louisiana after three years of informal commercial operations. The company also keeps commissioning trains at her Plaquemines LNG plant.
Mauritania, Senegal and Canada debuted in the LNG market in the second quarter. In April, British BP launched its floating LNG plant Greater Tortue Ahmeyim, located on the border of Mauritania and Senegal, into commercial operation. Capacity of Stage 1’s two trains is 1.3 MTPA . At the end of June, Canada launched train 1 of its first LNG plant. Its capacity - 7 MTPA.
USA remained to be the number one LNG supplier in the second quarter. Qatar and Australia are in the top three. Russia is confidently fourth.
As of 02.07.2025, there were 203 regasification terminals in the world with a total regasification capacity of 1069 MTPA.
Regasification capacities of 95.5 MTPA are expected to be commissioned this year. Y-o-Y growth is 10%. China’s share in capacity build up this year is 52%. Although many projects are delayed or even shelved. New regas projects are becoming more niche and focused on specifics of local areas.
China regained its leadership in LNG discharge in the second quarter. However, quarterly discharge volumes keeps falling. Japan and South Korea are in second and third places respectively. India is feeling more and more confident itself in fourth place.
As of 01.07.2025, there were 893 operational LNG carriers, including bunkering vessels, FSRU, floating LNG plants and floating storages with 60.0 MT of total cargo hold capacity. In 2025, LNG carriers with 7.8 MT of total cargo hold capacity are expected to be commissioned. It will be record-breaking volume. Y-o-Y increase is 56%.
On 26.03.2025, the EU ban on transshipment of Russian LNG in EU ports and its further re-export took effect. Its mainly affects one of key Yamal LNG export path with intermediate transshipment In Mountoir and Zeebrugge. So far, this EU self-ban does not restrict import of Russian LNG into EU itself. EU plans to introduce such the ban effective 2028.
Ukraine and USA have stopped the transit of Russian pipe gas through Ukraine to EU starting 01.01.2025. On 21.03.2025, Ukraine blew up the Sudzha gas measuring station. On March 28, with the assistance of USA, UK and France, Ukraine attacked this station with a rocker strike. As a result, the European market lost 41 mcm per day of pipeline gas, which created additional EU demand for US LNG in the amount of 11 MTPA (3% of worldwide LNG trade).
LNG spot price in East Asia (JKM) as of 04.07.2025 was 12.5 USD/MMBtu. At par with end of Q1 despite all turmoil.
Seaborne trade
In the second quarter, gas carriers continued to avoid the Red Sea area. On January 15, a temporary truce was reached between Israel, the United States and Britain on the one hand, and Palestine, Yemen and Iran on the other. As part of the truce, the safe passage of ships associated with Israel, the United States and the United Kingdom through the Red Sea was partially resumed. However, Israel's resumption of hostilities in Palestine on March 18 led to the violation of this truce and, accordingly, the resumption of restrictions in the Red Sea for ships associated with Israel and other States fighting on its side in Palestine. The consequences of getting into an LNG gas carrier differ significantly negatively from getting into a tanker or dry cargo ship, so gas carriers avoid dangerous areas of the Red Sea. At the same time, the passage of LNG gas carriers through the Suez Canal and the supply of LNG to the regasification terminals in the north of the Red Sea are safe.
In June 2024, during the war between Israel and the United States against Iran, there was a short-term panic regarding the location of gas carriers in the Persian Gulf.
The United States and the United Kingdom continue to use military technology to monitor LNG shipments from Russia's Arctic projects. Vessel tracking has already ceased to serve the original purpose of improving maritime safety, but has been put at the service of subordinating world trade to the dictatorship of the United States and partly Great Britain. This explains the dramatic decrease in transparency of shipping operations in the Arctic Ocean.
LNG plants
As of 30.06.2025, there were 47 LNG plants in the world, including partially idle ones, with a total operational LNG liquefaction capacity of 485 MTPA.
11 plants were completely or partially idle with a total non-functioning capacity of 42 MTPA. List of idle plants and trains:
Marsa el Brega LNG in Libya.
Yemen LNG.
Train 1 at the Atlantic LNG plant in Trinidad and Tobago.
Arctic LNG-2, one of the two Gazprom LNG Portovaya’s train, Cryogaz-Vysotsk plant in Russia.
Trains C, D, E of the Botang LNG plant in Indonesia.
Darwin LNG Plant and train 2 of the Northwest Shelf LNG plant in Australia.
Damietta LNG plant and Egyptian LNG plants in Egypt. EGAS at Idku discharges rare LNG cargoes from time to time.
As of 30.06.2025 trains at 24 plants (including expansion projects for existing plants) are under construction with new liquefaction capacity of 191 MTPA (39% of current operational capacity). Such an extremely high development rate for any industry indicates the upcoming changes in the industry in the coming years, which will be negative for LNG producers.
In 2025, LNG capacity is expected to be commissioned with a total volume of 49.5 million tons of LNG per year. This figure is close to a record high (51.8 in 2009). However, a much larger volume of liquefaction capacity is expected to be commissioned next year - 57.9 million tons/year. The United States dominates this process - it (including the US company's project in Mexico) will account for 62% of the capacity input in 2025, and 43% in 2026.
Starting in the summer of 2026, LNG will be in relative abundance, which will lead to lower prices, as well as a very beneficial situation for USA to attack its competitors on energy markets. Russia, Iran and to less extent Qatar is at risk.
Loading
According to Seala AI, the United States remained the number one supplier of LNG to the global market in the second quarter. Qatar and Australia are in the top three. Russia is the fourth.
USA
The United States was the largest producer of LNG in Q2 2025 is guaranteed to remain so in the coming years. The US LNG industry is living its best life.
LNG shipments from the United States in the second quarter amounted to 25.1 million tons. The volume of shipments was at the level of the first quarter and repeated the quarterly record. The utilization of existing capacities by the end of the quarter was 88%. To a certain extent, this disposal is explained by active commissioning work at new facilities and short-term restrictions on gas supply to existing plants.
LNG discharge at regas terminals, including Puerto Rico, amounted 307 kt in Q2.
Export poftfolio of US LNG was quite diversified in Q2 2025. Europe is focus of supply for US LNG.
In April, Calcasieu Pass LNG plant in Louisiana began formal commercial operation three years after the actual one. The owner of the plant, Venture Global LNG, founded by financier Michail Sabel, delayed the formal commissioning of its plant for many years in order to sell LNG at high spot prices in 2022-2024, rather than comply with previously concluded long-term contracts with formula prices. In terms of formula prices, LNG was significantly cheaper for customers during this period. In early April, against the backdrop of Trump's trade war, prices in the energy markets fell, which probably prompted Mikhail to begin fulfilling contractual obligations.
The list of buyers of “freedom“ molecules from this plant includes British Shell and BP, Polish PKN Orlen, Spanish Repsol, Italian Edison, Portuguese Galp, Chinese Sinopec and CNOOC. The total volume of binding supply contracts is 10 million tons/year (84% of the design capacity of the LNG plant).
The buyers are conducting legal proceedings against the company that owns the plant. At the same time, deliveries to China under these agreements will obviously not be carried out in view of China's retaliatory duties.
Venture Global LNG continued to commissioned new trains at giant Plaquemines plant. As of 30.06.2025, operating capacity of the LNG plant is 17 MTPA (trains 1-24). The commissioning of all 36 trains with a capacity of 0.56-0.74 MTPA will last until Q4 2026.
At the end of March, Cheniere Energy launched the first train of the third stage of its Corpus Christi LNG plant. The capacity of the line is 1.6 MTPA. The total capacity of the lines of the third stage is 11.5 MTPA. Its launch is expected to last until the end of 2026.
In April 2025, the US-based Kimmeridge gas company sold 24.1% of its subsidiary South Texas Holding Company, which produces gas in Texas and is developing an LNG plant construction project in Louisiana, to the Abu Dhabi-based Mubadala Fund (UAE), specializing in investments in the energy sector. Commonwealth LNG plant project includes the construction of six trains with a total capacity of 9.5 MTPA with their launch in 2029. For the Mubadala Foundation, this is the first project in the United States.
The United States continues to successfully monetize the crisis in Eastern Europe started in 2013 under Biden administration (vice president in 2009-2017, president in 2021-20225) and consequent elimination of Russian energy resources from the European market. Commissioning of US LNG plants is synchronized with the disconnections of Europe from Russian gas and LNG.
In Q2 2025 Trump administration continued the policy of Biden administration, but changed the goals of the main threats. Now Iran and its international gas trade are under political and military attacks. In Q1 2025, export of Iranian pipeline gas to Türkiye was banned. In Q2 2025 - to Iraq. At the same time, Trump is preventing the construction of gas pipelines from Iran to Pakistan and India. All this creates demand for LNG from these countries (Türkiye, Iraq, Pakistan, India). Trump's tariff war against everyone is forcing these countries to buy LNG from the United States.
On 02.04.2025, Trump imposed high import duties on almost all US trading partners. After that, Trump changed his approach to levying duties many times, but it was this event that became a key factor in uncertainty about future trade flows in the international LNG market. The Trump administration is forcing foreign countries to purchase LNG from the United States, as well as invest in future LNG projects in the United States, primarily the Alaska LNG plant.
In May 2025, the US Department of Energy published a study of the US gas market with the main conclusion that gas production will be sufficient for both domestic consumers and LNG exporters on the horizon until 2050. At the same time, DOE granted on 29.05.2025 export license for train 2 of Sempra’s Port Arthur LNG plant. Each train will have capacity 13.5 MTPA. This was the first case of permit issued after Biden's LNG pause.
In the coming years, the balancing of the Atlantic Basin market will be carried out by the United States /controlled countries due to the remaining supplies of Russian pipeline gas and LNG. Among the previously used mechanisms for disconnecting Russia from the global gas market:
Short-term permits for Türkiye to pay for gas purchased in Russia, supplied via the Turkish and Blue Streams. Blocking other transfers from Russia to Türkiye, which for some reason still go through US banks (for example, blocking JP Morgan's transfer of $ 2 billion to a Turkish bank as part of a loan for the construction of the Akkuyu nuclear power plant). Apparently, the Erdogan administration is not allowed to make such decisions on gas imports on its own and is kept on a short leash.
Attacks by British ships and Ukrainian UAVs of onshore compressor stations of these gas pipelines, including the blowing up of Sudga and the attack on the compressor station of the Turkish Stream.
Inclusion of ice class LNG carriers in hate lists of Great Britain, USA and EU.
An attempt to take control of the bankrupt owner of the Nord Streams.
Details of LNG shipment from the USA are available at the link.
Canada
Canada debuted on the LNG market on 29.06.2025. The first cargo was loaded that day onto LNG carrier Gaslog Glasgow.
Two trains of the Canada LNG plant with capacity of 7 MTPA each will be launched during 2025. Key destination market - Pacific region.
Two more local LNG plants are underway:
Woodfibre LNG plant near Vancouver with a capacity of 2.1 MTPA.
Cedar floating LNG plant next to Canada LNG with a capacity of 3.3 MTPA.
Mexico
Q2 2025 LNG exports from Mexico totaled 200 kt. Utilization of the only LNG plant so far (New Fortress Altamira) was 57%.
The construction of LNG facilities is under way in Mexico - as of 03.07.2025 - 4.7 MTPA capacity is under construction, and 27.2 MTPA is planned.
Q2 2025 LNG discharge amounted to 119 kt. Overall capacity of the regasification terminals is 17.9 MTPA. Q2 2025 utilisation was tiny 3%.
Trinidad and Tobago
Q2 2025 LNG loadings totaled 2.3 million tons. Utilization of operational capacities of the only LNG plant Atlantic LNG (11.8 MTPA without idle Line 1) amounted to 78%.
Traditionally, LNG from Trinidad and Tobago is shipped worldwide and has a diversified customer base.
Peru
Q2 2025 LNG loadings totaled 0.8 million tons. Utilization of the only LNG plant (4.4 MTPA) was 73%.
Q2 LNG was supplied to Europe and South Korea.
Qatar
Q2 2025 LNG loadings at QatarEnergy LNG’s combined QatarGas and RasGas plant amounted to 20.4 million tons. Plant utilization - 106%.
The attack by Israel and the United States with the indirect participation of the Persian Gulf countries on Iran in June led to serious turmoil in the spot market. Qatar's provision of its territory for an attack on Iran has reasonably caused the expectation of retaliatory actions from Iran. Jumping estimate of the geopolitical premium in the price of LNG led to jumps in the price of spot LNG with amplitude exceded 10%.
Qatar's main efforts are focused on the construction and contracting of future supplies for the expansion of the QatarGas plant with a total capacity of 49 MTPA. The launch of 6 trains will be carried out sequentially in 2026-2027.
Details of Qatar's exports are available at the link.
UAE
Q2 2025 loadings at the only LNG plant Das Island (7.6 MTPA) amounted 1.4 million tons. Utilization was 74%.
Discharge at regasification terminal in Jebel Ali (Emirate of Dubai) amounted to 225 kt. Traditionally, discharges at this terminal peak in the third quarter of each year during the heat wave.
A single case of ship-to-ship transhipment of LNG cargo was recorded in anchorage of Khor Fakkan.
Emirate of Abu Dhabi keeps increasing its presence in the global LNG market. Primarily it happens via abroad M&A. Main agents of abroad presence are ADNOC and the Mubadala Investment Fund. Key transactions in Q2 2025:
Purchase from US gas company Kimmeridge of 24.1% of its subsidiary South Texas Holding Company, which produces gas in Texas and is developing a project to build the Commonwealth LNG plant in Louisiana (9.5 MTPA) with its launch in 2029.
Purchase of 40% of Talimarjan gas thermal power plant in Uzbekistan.
Development of LNG bunkering in UAE ports on basis of own LNG bunkering vessel Green Zeebrugge.
Offer to purchase Australian gas company Santos.
The second LNG plant in the country, Ruwais, is expected to be launched in 2029. The plant's capacity will be 9.6 MTPA.
Oman
Loadings at the only LNG plant (11.4 MTPA) amounted to 2.6 million tons in Q2 2025. Utilization of the design capacity was 91%.
Key importers of Q2 resource are South Korea, China (including Taiwan), Japan and India. Neighboring Kuwait consumes two cargoes per months, which is traditional for the warm months.
Australia
LNG loadings at Australian plants totaled 18.4 million tons in Q2 2025. This was the lowest level for the entire observation period (starting from the third quarter of 2022). Utilization of operational capacities (excluding long-term idle) - 90%.
In Q2 2025 Australia traditionally became the number one LNG supplier to the world's two largest LNG importers, China and Japan.
Northern Australian LNG projects are facing a steady decline in gas production.
Darwin LNG plant (3.7 MTPA) has been idle since November 2023. The launch of the Barosso gas field in the second half of 2025, whose gas reserves 2P (total proven and probable reserves) are estimated at 110 bcm, will allow the restart of the Darwin LNG plant.
Train 2 of Woodside Energy’s Northwest Shelf LNG plant (2.5 MTPA) continued to be idle due to economic reasons. The launch of the second stage of development of the Waitsia gas field in the third quarter of 2025 will provide additional gas resources for the Northwest Shelf LNG plant.
The Scarborough natural gas field, located in the Carnarvon Basin, about 375 km off the coast of Western Australia, is expected to be commissioned in 2026. The development includes the installation of a semi-submersible floating production facility moored at a depth of 950 m, connected by a pipeline with a length of about 430 km to the second line of the Pluto LNG plant with a capacity of 5 million tons/year at an existing onshore facility.
Ichthys LNG plant is expected to be shut down for 51 days in Q3 2025 - from August 19 to October 9. It will reduce exports by 1.2 million tons during this period.
Details of Australia's exports are available at the link.
Papua New Guinea
Q2 2025 loadings at the country's only LNG plant (8.3 MTPA) quarter amounted to 2.2 million tons. Utilization of the design capacity was 106%.
All cargoes go to neighboring East Asian countries - China (including Taiwan), Japan and South Korea. In Q2 one cargo also went to Thailand.
Brunei
Q2 2025 loadings at the only LNG plant (7.2 MTPA) amounted to 952 kt. Utilization of the design capacity was 53%.
All cargoes go to neighboring East Asian countries - China (including Taiwan), Japan and South Korea. In Q2 two cargoes also went to Thailand.
Indonesia
LNG loadings at the LNG plants amounted to 4.3 million tons in Q2 2025. Utilization of operational capacity (excluding long-term idle) was 79%.
LNG discharge at own regasification terminals amounted to 1.4 million tons (34% of the country's production).
Indonesia still prohibits supply of foreign LNG to its terminals, reducing the impact of external risks on the domestic gas market.
In March 2025, Indonesian Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources cancelled previously signed contract between Indonesian company Conrad Asia Energy and Singapore's Sembcorp Industries, which is developing Mako field, for supply of 767 mcm / year of gas from this field to Singapore starting in 2027 for 10 years.
Malaysia
LNG loadings at Malaysian plants totaled 5.2 million tons in Q2 2025. Utilization of the design capacity (32 MTPA) was 50%.
Discharge at Malaysian regas terminals amounted to 773 kt (15% of domestic LNG production).
Details of Malaysia's exports are available at the link.
Russia
According to statements by Deputy Prime Minister of the Russian Government Alexander Novak, the LNG export plan for 2025 is 33 million tons, at the level of 2024.
In mid-April, the Energy Strategy of the Russian Federation until 2050 was adopted, which sets benchmarks for LNG exports:
2030 - 103 million tons of LNG.
2036 - 130 million tons of LNG.
2050 - 175 million tons of LNG.
LNG production in Russia is stable and withstands moderate pressure from the United States and the EU. However, all new development projects have been put on pause due to the much more critical level of pressure on them from these countries. From a resource, technological and production point of view, Russia (and above all Novatek) is ready to export such volumes of LNG in the long term. At the moment, everything depends on the political willingness of foreign buyers to import Russian LNG.
LNG loadings amounted 7.7 million tons in the second quarter. This indicates 111% utilization of the design capacity of operational capacity (excluding long-term idle trains).
5.2 million tons were shipped from Yamal LNG (Sabetta port). Loadings are at a stable level.
In the second quarter, the intermediate transshipment scheme at the Murmansk shore was traditionally actively used - 1.0 million tons (19% of all volumes) were delivered according to this scheme.
After overloading in Murmansk, most of the volumes go to China.
On March 26, 2025, the EU ban on transshipment of Russian LNG in EU ports and its further export began to take effect. This will mainly affect one of the key LNG export schemes from Yamal LNG with intermediate transshipment through the French port of Montoire and the Belgian port of Zeebrugge. This EU self-ban does not yet restrict the export of LNG directly to the EU, followed by its regasification at terminals. In the second quarter, Russian LNG supplies to these ports continued for the time being. In the first half of the year, 2.1 million tons of LNG were delivered to these ports.
The main destination for re-exported LNG of all origins from Montoire and Zeebrugge is China.
2.3 million tons was loaded at Sakhalin-2 (Prigorodnoye port). Most of LNG cargoes goes to China and Japan. Japan continues to receive so-called “permits” from the United States to import LNG from Sakhalin-2. There were also shipments to South Korea and Vietnam.
Train 1 of Arctic LNG-2 continued to be idle due to the lack of LNG buyers. Cargoes from Arctic LNG-2, shipped as part of the pilot launch of the Train 1 of Arctic LNG-2 in H2 2024, did not find their buyers as of 07.07.2025.
On 26.06.2025, LNG carrier ”Iris“ (formerly “Northern Sky“) apparently loaded a cargo at Arctic LNG-2 and is heading for transshipment in Murmansk. This loading was the first since 05.10.2024. As of 30.06.2025, there were no other shipments. Even the operation of one plant line involves loading a gas carrier every 4 days.
Exports from Russia's medium-tonnage Baltic projects in Vysotsk, Leningrad Region, were halted in Q1 2025 due to EU rejection and US pressure on third countries.
Last export cargo was shipped from Gazprom LNG Portovaya on February 13. Moreover, the last two cargoes for export are still on the Pearl (formerly Pskov) and Valera LNG carriers in the Russian territorial waters of the Gulf of Finland. Since then, the plant has loaded three 76 kt cargoes to the Marshal Vasilevsky. All cargoes were delivered to Kaliningrad region of Russia. This indicates chosen tactics of the plant for the coming years: one of the trains has been shut down, the other will ship LNG cargoes using Marshal Vasilevsky approximately every 37 days with their subsequent regasification by the same Marshal Vasilevsky.
The last cargo from Cryogaz-Vysotsk left on February 17 and was delivered to Zeebrugge, Belgium. There were no shipments in the second quarter.
Details of shipments of Russian LNG are available at the link.
Norway
Q2 2025 loadings at the country's only large-tonnage plant Hammerfest Snøhvit (4.2 MTPA) amounted to 299 kt. Deliveries were carried out only in April. The achieved utilization is only 28%. Almost all of the LNG was supplied to the EU and one cargo went to Egypt.
The low-tonnage Risivika (330 kt per yer) operated at its design capacity and provided LNG bunkering and small parcels for local consumers.
Mozambique
Q2 2025 loadings at the only LNG plant Coral South (3.4 MTPA) amounted to 1.0 million tons. This indicates 118% utilization.
In December 2024, the final investment decision was made on Coral North floating LNG plant project. The country's second floating LNG plant with a planned capacity of 3.4 MTPA is expected to be commissioned at the end of 2027. Owners of both Coral projects are the Italian Eni, ExxonMobil from the USA, Chinese CNPC, South Korea’s the Korean Gas Corporation, UAE’s ADNOC and the local Empresa Nacional Hydrocarbons. Mozambique's share in these projects is tiny 10%. On top of this, LNG sales of ENH’s 10% share are controlled exclusively by Dutch Vitol.
Construction of Mozambique LNG Zone 1 offshore plant (13 MTPA) is frozen as of 08.07.2025. Construction was halted due to a standoff with local population. This project is 100% controlled by foreign companies from France, Japan, India and Thailand, which is probably the real reason for the discontent of local communities.
In addition, ExxonMobil’s Rovuma LNG (18 MTPA) project is under development. Final investment decision is expected in 2026. However, there is limited economic sense nowadays for US company to develop LNG project abroad and compete with domestic US LNG projects. The only exception if ExxonMobil will grab almost all profit of this project.
Thus potential Mozambique’s liquefaction capacity is up to 38 MTPA.
Angola
LNG exports from Angola are growing in 2025 due to increased gas production at Sankha field. Q2 2025 loadings amounted to 929 kt. Utilization of the only LNG plant (5.2 MTPA) amounted to 71%.
The increase in gas production at this depleted oil field has provided 2.3 mcm per day (0.8 bcm per year) of additional resource for Angola LNG. At the second stage of production improvement at this field, additional supplies to the LNG plant are expected in the amount of 6 mcm per day (2.2 bcm per year). Operational capacity of the Angola LNG plant is 5.2 MTMA, which is equivalent to 7.1 bcm per year of natural gas.
Previously, Angola LNG's main resource was associated gas from offshore oil platforms. Natural decline in oil production led to a decrease in the associated gas resource for the LNG plant. New gas consortium plans to add up to 12 mcm of gas for the LNG plant from the pure Quiluma and Maboqueiro gas fields, which will ensure full utilization of the plant and give feasibility for its expansion.
Republic of the Congo
The first floating LNG plant Tango (0.6 MTPA) continues stable shipments. 141 kt were loaded in Q2 2025, which indicates 94% utilization of the plant.
Preparations are underway to launch the second LNG plant with a capacity of 2.4 MTPA. Commissioning is expected in late 2025 - early 2026. The plant's resource base is the Nene Marine offshore oil and gas field, which is already operating.
Equatorial Guinea
Punta Europe floating LNG plant (3.7 MTPA) continues stable shipments. 700 kt were loaded in Q2 2025. Achieved utilization is 79%.
Cameroon
Cameroon floating LNG plant (2.4 MTPA) continues stable shipments. Q2 2025 loadings amounted 250 kt, which indicates a low 42% utilization of the plant.
Hilli Episeyo (7382720), which is the basis of this LNG plant, will finish its work in Cameroon in December 2026 and will be moved to Argentina for a new GLNG project. In Q2 2025, the vessel was chartered for 20 years for this new project.
Nigeria
Loadings at Nigeria LNG, the only LNG plant, amounted to 3.9 million tons in Q2 2025. It is record volume since start of tracking by Seala AI (since Q3 2022). Utilization of the design capacity (22.2 MTPA) is 70%.
Mauritania and Senegal
In February-April 2025, the British BP commissioned the first stage of its floating LNG plant Greater Tortue Ahmeyim on the border of Mauritania and Senegal. In October 2024, BP’s British Sponsor LNG carrier delivered to the plant LNG cargo necessary for technical start-up of the plant's facilities, and in February - April, the first three small LNG parcels were produced at the plant. Commercial operation began on April 17. Combined capacity of the four trains amounts 2.5 MTPA. It is expected that commissioning will be done by end of 2025.
Q2 2025 loadings amounted to 448 kt. This means that as of 30.06.2025, two of the four trains are operating.
Algeria
Loadings at the country's two LNG plants amounted to 2.5 million tons in Q2 2025. Utilization of design capacity (25.5 MTPA) - 39%.
The main exports of Algerian natural gas are still carried out through pipelines to Spain and Italy.
Details of Algerian exports are available at the link.
All other countries exported less than 2 million tons of LNG in Q2 2025. Detailed export statistics by country are available at the link.
Regasification terminals
As of 08.07.2025, there were 203 regasification terminals in the world, including terminals with temporarily unavailable FSRU, with a total regasification capacity in the amount of 1,069 MTPA.
The regasification capacity exceeds the LNG production capacity by 2.2 times. A significant part of regas terminals is designed to manage risks of local energy systems and import LNG only when necessary. List of such typical risks includes:
Increased demand during heating season. Relevant for UK, EU, Türkiye, China, Japan, and South Korea.
Increased demand during the hot season. Relevant for Egypt, the Middle East, India and Southeast Asia.
Shortage of hydroelectric power generation due to droughts. Relevant for Brazil and partly Norway.
Shortage of wind power generation on certain days and seasons. Relevant for EU.
Reserve in case of interruption of pipeline gas supplies. Relevant for EU.
A reserve in case of temporary poor environmental conditions and the need to reduce the share of coal generation for a while. Relevant for China and South Korea.
Trading companies also build regasification terminals to create the necessary infrastructure conditions for portfolio (price) optimization of gas and other fuel purchases for TPP. This approach is especially relevant for large markets such as China and EU.
Due to regas project delays the peak of commissioning of new capacites shifted from 2024 to 2025. Regasification capacity of 95.5 MTPA is expected to be commissioned this year. Annual increase - 10%. China’s share in new 2025 capacities - 52%.
Many projects are delayed or even shelved. New regas projects are becoming more niche and focused on specifics of local areas.
Discharge
According to Seala AI, China once again became the leader in LNG discharge. However, quarterly discharge volumes keeps falling. Japan and South Korea are in second and third places respectively. India is feeling more and more confident itself in fourth place.
China
Mainland China
In early January 2025, the United States launched preliminary attack on China's LNG industry, including China Ocean Shipping Corporation (COSCO), China National Offshore Oil Corporation (CNOOC) and Chinese State Shipbuilding Corporation (CSSC). This attack marked the beginning of the US trade war against China in the LNG industry as part of wider attempt to avoid imminent default on government debt (37 trillion USD / quadrillion 2.9 RUB / 136 trillion AED / 266 trillion CNY / quadrillion 3.2 INR ) as of 08.08.2025).
COSCO is the world's leading shipping company. Its fleet of LNG gas carriers includes 45 operating LNG carriers and 40 LNG carriers under construction. Total capacity of the company's current and prospective fleet of LNG carriers is 6.5 million tons of LNG. It is equivalent to 12% of the current fleet of LNG carriers in the world. In 2024, COSCO LNG carriers serviced shipments for PetroChina, Sinopec, ENN and QatarEnergy LNG.
CNOOC’ share on Chinese LNG imoirt market is 50%. It owns 6 regasification terminals in China with total regas capacity 32 MTPA.
Chinese shipbuilders are the world's second largest supplier of LNG carriers to the global market. For more information, see the section about the fleet. CSSC, including its subsidiary Hudong-Zhonghua, is the largest shipbuilder of LNG gas carriers right now.
On 4.02.2025, China introduced countermeasures against imports of LNG and other goods from the United States as part of a mirror response to tariffs imposed by Trump administration on all Chinese exports to the United States. The tariff on LNG imports from the United States to China was set to 15%.
On 04.04.2025, China imposed a 34% tariff on all imports from the United States. Thus, the LNG tariff rate increased from 15% to 34%.
On 10.10.2025, China raised the tariff on all goods to 84%.
Import tariff of such value halted LNG shipments from the United States to China and led to a mutual redirection of flows starting 07.02.2025. As of 08.07.2025 no US LNG cargo has been imported in China since then.
It is worth noting that long-term contracts for LNG supply from USA to China are still valid:
Venture Global Calcasieu Pass LNG with Sinopec for 1 MTPA.
Venture Global Calcasieu Pass LNG Company with CNOOC for 0.5 MTPA.
Cheniere Energy with ENN for 0.9 MTPA.
Cheniere Energy with CNPC for 0.9 MTPA.
China continues to dominate in regas capacity newbuild. China continues to rely on its gas infrastructure and actively develop it. China is flexible in LNG purchases and does not critically depend on it — balancing is carried out by pipeline gas, coal, and hydroelectric power plants.
As of 08.07.2025, there are 35 operating regasification terminals in China with total capacity 149 MTPA.
The year 2025 is expected to be a record year for the commissioning of regasification terminals in China. However, there is already some regional surplus of regas capacity. It led and keeps leading to low utilization levels for new and existing terminals. Practice of accelerated construction of facilities in a certain industry in China, followed by itsunderutilization, is quite common and regularly repeated in China. Therefore, the growth of regasification capacity in China will not necessarily lead to an increase in LNG imports in 2025 and beyond.
LNG shipments to China totaled 14.2 million tons in the second quarter. This indicator is the lowest for the entire observation period. The previous one was in the last quarter - 14.4, the record quarterly import volume was 20.9 million tons in the first quarter of 2024. Utilization of regasification terminals in the second quarter was 37%.
The volume of physical re-export of LNG from China amounted to 340 thousand tons in the second quarter.
It is worth noting that natural gas supplies from Russia to China via the Power of Siberia are growing every quarter. It is expected that designed capacity (38 bcm per year) will be reached in Q4 2025. In 2024, 31 bcm were delivered. Thus, in 2025, the Chinese market will have an additional 5-6 billion cubic meters of natural gas, which is equivalent to 332 kt LNG per month.
Taiwan province
Q2 2025 LNG imports amounted 5.3 million tons. Import volumes have been stable for a long time. Utilization of the regas terminals (20.0 MTPA) was 106%, the highest in the world.
In early April, after Trump administration imposed new tariffs on almost all countries, Ministry of Economic Affairs of Taiwan Province of China contacted Trump Administration with a proposal to increase US LNG purchases by two to three times in an attempt to reduce or eliminate the tariffs imposed. In 2024, Taiwan imported 2 million tons of LNG from the United States, which accounted for 10% of Taiwan's LNG purchase portfolio.
Japan
Q2 2025 discharges amounted 13.3 million tons. It is the lowest figure for the entire observation period (since the third quarter of 2022). Utilization of regas capacity (216 MTPA) was 25%. Regas terminals in the country are in excess. Excess capacity created for insuring that peak seasonal and regional demands will be met, as well as overcoming problems with nuclear and coal generation.
Largest LNG suppliers to Japan in Q2 2025:
Australia - 6.1 million tons
Malaysia - 1.7 million tons
Russia - 1.1. All shipments were from Sakhalin.
Japan has a very diversified supplier base - in the second quarter, shipments were made from 12 countries. Many of these supplies are controlled by Japanese oil and gas companies, including ownership of gas carriers and stakes in LNG plants.
Due to the lack of significant economic growth and the extinction of the Japanese population, domestic gas consumption stagnates. Recommissioning of nuclear power plants that were shut down after Fukushima in 2010 has an additional impact to decrease in LNG import. However, there are delays of restart dates of power units due to regulatory issues. So in the second quarter, it became known about the postponement of the launch of units 6 and 7 of the Kashiwazaki NPP.
Japanese gas companies are developing the trading of long-term contracted LNG volumes to third countries. This includes investing in regasification capacities in Southeast Asian countries, as well as pressure on non-Japanese owned LNG suppliers to cancel destination clause in long-term contracts. Due to huge Japanese LNG fleet and the emerging optionality in gas supply directions, it is reasonable to expect further increase in the international trading activity of leading Japanese gas companies.
South Korea
Q2 2025 LNG import totaled 10.9 million tons. Utilization of the design capacity of regas terminals (146 MTPA) is 30%.
Key Suppliers:
Australia - 3.7 million tons
Qatar - 1.7
Malaysia - 1.2
USA - 1.2
Oman - 502 kt
Russia - 474 kt
The structure of LNG suppliers to South Korea is very diversified and consisted of 19 countries in the second quarter.
Singapore
In the second quarter, 1.5 million tons were shipped to Singapore, of which 160,000 were re-exported and 135,000 were sold as a bunker.
Utilization of the regasification terminal (11 MTPA) was 44%.
Details of the import and re-export of LNG by Singapore are available at the link.
Thailand
Gas-fired thermal power plants account for more than half of power generation in Thailand. Therefore, LNG demand strongly depends on seasonality of electricity demand and availability of cheaper sources of electricity (primarily hydroelectric power plants).
The period from March to May is the peak period in terms of electricity demand.
LNG imports in April were affected by the problem of fullness of LNG storage facilities at terminals and electricity imports from Laos due to the high generation of its hydroelectric power plants.
Q2 2025 LNG imports amounted to 2.6 million tons. Utilization of the terminals (19 MTPA) was 55%.
Bangladesh
Q2 2025 LNG imports amounted to 1.7 million tons. Utilization of rwo FSRUs (7.5 MTPA) is high 91%.
India
Q2 2025 LNG imports totaled 6.5 million tons. Utilization of the design capacity of the terminals (51.5 MTPA) was 50%.
Qatar continues to be the leading supplier of LNG to India and accounts for about half of Indian LNG market. USA and UAE are in top 3.
It is worth noting the statement made by the Indian Minister of Energy while visiting USA that India will not import LNG from the Arctic LNG-2 project due to threats from the United States. The success story of Russian offshore oil exports, where India has become the dominant buyer of redirected supplies, has not been repeated with Russian LNG.
Pakistan
Main consumers of LNG in the country is gas-fired thermal power plants. Gas-fired thermal power plants compete in generation stack with sun power plants, which are being actively developed. As of 03.07.2025, Pakistan has 14.7 GW gas-fired TPP. This is equivalent to 23 MTPA in case of base loading, excluding repairs. 2024 LNG import volume amounted 8.2 million tons.
Pakistan has a population of 242 million people. Economic growth rate is 3.2% (of which 1.6% is due to population growth). The territory of Pakistan is poor in terms of hydrocarbons reserves. Pakistan has huge potential for LNG and pipeline gas imports in the future. Per capita energy consumption remains at a very low level and has a high potential for growth. But the poverty of the population and high risks for infrastructure projects hinder the growth of LNG imports.
Pakistan subsidizes domestic gas and electricity prices. Under IMF pressure Government of Pakistan raised in 2025 gas and electricity prices in order to reduce budget expenditures. This is expected to reduce the demand for electricity. In addition, this will reduce the demand for LNG imports in H2 2025 and beyond, with an additional impact from the growth of installed SPP capacity and economic prioritization of coal-fired generation over gas-fired.
Q2 2025 discharges amounted 2.0 million tons. Utilization of two operating terminals (10.5 MTPA) was 78%.
All cargoes in Q2 came from Qatar. Pakistan has two long-term contracts with Qatar for the supply of 5.7 MTPA (1.4 million ton per quarter).
There is also a long-term contract with Eni for the supply of 700 thousand tons per year (175 thousand tons per quarter).
In the second quarter, Pakistani LNG importers cancelled 16 shipments of LNG cargoes under long-term contracts. Of these, Eni - 11, QatarEnergy - 6.
There are reports of delays in payments by Pakistani companies for already delivered LNG cargoes. However, it is unlikely that this will be a constraint for Qatar Energy due to Qatar's interest in strong bilateral relations with Pakistan.
Pakistani importers (PSO, Pakistan LNG) reported that they are looking for options to resell some of the Qatari LNG cargoes due to its current unprofitability for the companies.
Iran
In June 2025, Iran successfully launched the fourth gas purification complex at the 14th phase of the South Pars gas field. Iran's gas production continues to grow rapidly. On top of this Iranians build new facilities using their own technological and financial resources.
Iraq
In April, the United States banned Iraq from continuing to import Iranian natural gas. It is difficult for a theoretically sovereign state to disobey the hegemon, but as matter fo fact import gas still flows from Iran.
As of June 2025, an agreement is in effect between Iran and Iraq for the supply of 55 mcm per day of pipeline gas (20 bcm per year). In June export shipments to Iraq shrinked to 25 mcm per day due to growing domestic consumption in Iran. Gas shortages in Iran during peak consumption periods (frosty weather in the northern part in winter and heat in the southern part in July and August) are an additional risk factor for Iraq. Due to this decrease in gas supplies from Iran, electricity generation in the country fell by 15% in June, even with the starting up of reserver diesel generators.
Iraq is looking for free FSRU to start regasification as an alternative to importing Iranian pipeline gas for the needs of its thermal power plants. Heat wave in July and August traditionally causes the country's energy system to operate at maximum levels. As of 03.07.2025, there are no FSRU operating in Iraq.
Kuwait
Q2 2025 discharge volume amounted to 2.2 million tons. Utilization of the only regas terminal (11.3 MTPA) was 78%.
Bahrain
In mid-April, the regasification terminal in Bahrain resumed operations after being idle since 2019. The first vessel to be unloaded after the break was Seapeak Bahrain. In total, three LNG shipments totaling 223 thousand tons were unloaded in the second quarter.
Egypt
The growing demand for gas coupled with shrinking domestic natural gas production, has moved Egypt from the category of exporters to the category of importers.
Both of the country's LNG plants, Damietta LNG and Egyptian LNG, are idle due to lack of resource. ELNG ships rare LNG cargoes which indicates partial operation of one of its trains. Only one cargo was shipped in the second quarter.
To meet the demand for gas, Egypt is actively leasing FSRUs. Location of FSRUs:
Ain Sukhna is key port for LNG discharge.
Damietta has started regasification in June 2025.
The main Egyptian regasification hub has been formed in Ain Sukhna: FSRU Höegh Galleon since 2015, FSRU Energos Power and Energos Eskimo since the summer of 2025, FSRU Höegh Gandria starting November 2026.
Earlier in 2022-2025, Egypt used Aqaba industrial port in neighboring Jordan to regasify some LNG shipments. Starting in the summer of 2025, FSRU Energos Eskimo moved from Jordan’s shore to Egyptian.
In June-November 2025, Ertugrul Gazi will be leased from Türkiye for a short-term lease. This is an interesting attempt to use a single FSRU to meet peak demand at different times and locations: heat period in June-September in Egypt, heating period in December-February in Turkey.
Q2 2025 LNG discharges amounted to 1.1 million tons of LNG. This is the fourth consecutive quarter with LNG unloading in Egypt of over 1 million tons.
Egypt is expected to charter up to 100 spot LNG cargoes in H2 2025 to meet growing demand and falling production. As of March 2025, production stands at 117 mcmc per day and is falling rapidly (a 35% drop over the year). In 2023-2024, rolling power outages were carried out due to gas shortages.
Türkiye
In March 2025, Türkiye, Turkmenistan and Iran signed a geographical gas swap deal. Turkmenistan supplies gas to northeastern Iran, and Iran, in turn, supplies gas to Türkiye via the Iran-Türkiye gas pipeline. Contract volume is 1.3 bcm per year. The term of the contract is 1 year. Gas importer at Türkiye's side is BOTAŞ. The bombing of oil and gas facilities in Iran by Israel and NATO in June 2025 did not stop supplies under this contract.
On April 9, 2025, Ukrainian and EU UAVs attacked Korenovskaya compressor station of the Turkish Stream. This was the second attack (the first was on January 11). After Türkiye's diplomatic intervention, no further attacks on the gas pipeline has happened.
In June 2025, the Turkish state-owned company BOTAŞ announced completion of the construction of an export pipeline to Syria. Türkiye continues economic integration of Syria within the framework of its Turan policy. The border point of gas supply is Yavuzlu/7000. The pipeline's capacity is 6 mcm per day.
Q2 2025 discharge amounted to 1.1 million tons. A 5-fold decrease after Q1. Traditionally, Türkiye actively imports LNG only during the cold months from November to March.
EU and UK
Pipeline gas import
For Russophobic reasons, the European Commission requires all EU countries, as well as states planning to join EU, to begin terminating gas supply agreements with Gazprom Export. In Q2 2025 the European Commission presented the following action plan:
Self-restriction of EU countries on conclusion of new supply agreements for pipeline gas and LNG starting from 01.01.2026.
“Termination” of short-term agreements by 17.06.2026.
“Termination“ of long-term agreements tby 01.01.2028 for all EU countries except Slovakia and Hungary.
As of 09.07.2026, this plan has not been agreed.
Since January 2025, Turkish Stream has been the only Russian gas supply channel to EU. In H1 2025, Russian supplies to EU via this route (including re-export of gas outside the EU) amounted to 43 mcm per day, which is 10% of 2021 import volumes. Of these, 21 mcm per day goes to Hungary, 7 - to Slovakia, 15 - to Serbia (including re-exports to non-EU Balkan countries), and 1 - to Greece. Some of physical molecules of Russian gas are likely to enter Ukraine from Hungary and Slovakia as part of Ukraine's commercial imports of European gas.
According to the terms of the agreements, European companies must pay fines for non-taking of gas (take-or-pay clause). The European Commission does not want to pay fines and is looking for ways to sign some kind of paper, according to which unilateral termination of international agreements without penaltieswill be considered “legitimate” in EU. Pocket Stockholm Arbitration Court is likely to be involved in this process. There is already the precedent for “legitimizing” termination of similar contract between Ukraine and Russia without paying contract amount of penalties by Ukraine. This process will finally disconnect EU gas market from supplies from Russia, which will bring additional losses to EU companies and residents and lead to continued stagnation of energy-intensive industries in EU. Even more damage will be carried on by Gazprom. It was gas sales to EU that ensured low level of domestic gas tariffs, as well as Gazprom's generous social program.
In July 2025, Greek DEPA (ΔΕΠΑ) concluded a pre-trial agreement with Gazprom Export regarding the retrospective revision of the supply price under the current gas supply agreement.The agreement was signed in January 2022 and is valid until the end of 2026. The annual volume of supplies under the current agreement is 2 bcm (5 mcm per day). The agreement contains the ”take or pay" clause. The formula price has a basic reference to the TTF index (80% of the price) and crude oil quotations (20%).
Gas stocks at UGS
Gas reserves are a key indicator of the balance of the European gas market. The compliance of gas reserves with the target level determines the necessary rates of their replenishment.
Since June 2022, the target level of gas reserves in EU’s UGS has been determined mostly by the European Commission (Gas storage regulation). Some countries also have additional national requirements set by local governments.
Storage practices in Europe has undergone major changes lately. UGSs now are playing much more important role in ensuring meeting winter peak demand due to lower volumes of pipeline gas incoming to European market. Seasonality is becoming more and more evident in this market. The accumulated reserves at the beginning of the gas winter are getting bigger and bigger every year, however, the rate of gas consumption during the gas winter is also breaking records every year.
According to the current version of the regulations as of 02.07.2025, the following basic standards apply for target reserves: the peak level of active gas reserves in the period from October 1 to December 1 should be 90% of the total storage capacity of national UGSs. There is also a threshold of 5% of allowable deviation from the target. As of 02.07.2025, this corresponds to 92.7 bcm in the EU’s UGS (85% of 109 bcm active capacity) plus 1.5 bcm in UK’s UGS. In total, 94 billion in the period from the 274th to the 335th day of the year (see graph at the top).
As of 01.07.2025, reserves in the UGS of EU and UK amounted to 64.2 bcm. Net gas injection into UGS in Q2 2025 amounted to 29.0 bcm, which is equivalent to 9.7 bcm per month or 7.0 million tons of LNG per month, on average.
The required replenishment rates determine the LNG import plan. Since 2022, LNG (primarily from the United States) has been the balancing resource of the European gas market and has replaced Gazprom in this regard.
LNG import
External LNG imports to EU and UK, excluding regional cabotage, totaled 28.0 million tons in Q2 2025, which is equivalent to an average of 9.3 million tons per month. Thus, in the second quarter, 75% of LNG imports were pumped into UGS facilities in preparation for the gas winter.
The largest importers in Q2 2025:
France - 5.6 million tons, which is equivalent to 20% of total imports.
Spain - 4.9 (17%).
Netherlands - 4.1 (15%).
In the second quarter, USA became the leading supplier of LNG to EU and UK - 15.6 million tons. The share of total foreign imports is 56%. LNG imports from the US to EU and UK are pretty much stable after its rapid growth in 2022. EU and UK are critically energy dependent on USA. As a result of the launch of new US LNG capacities (Plaquemines, the third phase of Corpus Christi) and US trade deals with UK and EU, we should expect a further increase in the US share in the EU and UK gas market at the expense of Russia and then Qatar.
Russia took the second place in Q2 2025 with 4.2 million tons and share of 15%.
France are imported 1463 kt of LNG in Q2 2025.It is import LNG under long-term contract of TotalEnergies with Yamal LNG (2.6 MTPA till 2032), where it also holds 20% share in Yamal LNG plant itself. Previously TotalEnergies defaulted on its obligation under long-term contract (equity entitlement) with Arctic LNG 2 (2 MTPA till 2044), where it holds 10% share. In case of more EU attacks on Russian LNG industry, further French defaults on gas contracts or within future settlement of 200+ bEUR debt of EU to Russia, TotalEnergies presumably could lost its 20% share of Yamal LNG and 10% of Artic LNG 2.
Spain imported 923 kt from Russia in Q2 2025. It imports under long-term contract of Naturgy with Yamal LNG (2.5 MTPA till 2043).
Some of these volumes were re-exported further outside EU. After the strengthening of bans on the re-export of Yamal gas from EU ports, it is reasonable to expect new logistics schemes and a formal reduction in the share of Russian LNG in EU and UK market.
Qatar continued to occupy the number three position in the ranking of LNG suppliers to EU and UK with a volume of 2.6 million tons in Q2 2025 and a share of 9%. Qatar is consistently increasing its penetration into the European gas market, including long-term lease of regasification facilities. Thus, QatarEnergy controls the supply chain from natural gas wells to wholesale gas sales in the countries of North-Western Europe. In fact, this strategy repeats Gazprom's previous strategy in the European market and, accordingly, has the same risks.
Regas terminals
As of 02.07.2025, there are 41 terminals in EU and UK with a combined regasification capacity of 210 MTPA, which is equivalent to 17.5 million tons per month. Terminals’ utilization was 53% in Q2.
The current capacity of the regasification terminals in Germany is 18.8 MTPA, which is equivalent to 1.6 million tons per month. At the same time, the maximum volume of LNG imports in Germany was reached this June and amounted 753 kt (utilization rate of 48%). Germany is facing an oversupply of regasification capacity. Moreover it is relatively expensive FSRUs.
On 16.05.2025, the second FSRU (Excelsior, 9239616) began operating in the German port of Wilhelmshaven. It is planned that 1.9 bcm of gas will be delivered through this terminal in 2025. The plan for 2026-2027 is 4.6 bcm per year.
The first FSRU in Wilhelmshaven (Höegh Esperanza, 9780354) started operations in December 2022. All the LNG supplied to the terminal is from the USA.
At the same time, Egypt leased one of the idle German FSRU located in the port of Sassnitz (formerly Mukran).
Details of LNG imports by EU countries are available at the link.
Ukraine
Since 2025, the Ukrainian gas market has completed its strategic integration to the EU gas market and has become a part of it.
Gas reserves in Ukraine continue to be actively replenished and as of 01.07.2025 amount to 3.4 bcm. Utilization of storage capacity is 11%. This is an anti-record for the entire time of observations, but this volume is enough for shrinked Ukrainian domestic gas market.
Thus, the target volume of gas injection for this summer is 7.5 bcm, which is equivalent to 42 mcm per day. In Q2 2025 net injection amounted to 2.6 bcm, which indicates an interim failure to meet the injection plan (by 31%). If money wis found somewhere, all the necessary volumes can be easily pumped in Q3 2025.
It is symbolic and ironic that exactly 7.5 bcm per six months was amount of gas flowing from Russia to Ukraine. After the explosion of the gas measuring station in Sudzha, the physical scheme of gas supplies for injection into UGS has changed. In all previous years, Russian molecules of gas was pumped into UGS. This summer, the entire volume of gas will have to be imported from the western points of entry into the GTS of Ukraine. This import scheme and the higher market gas price this year will further increase the burden on Ukraine's budget to finance these supplies. It is the lack of money to buy gas that is the main constraint in accumulation of gas reserves (and similarly with thermal coal reserves) in Ukraine. Logistical difficulties are important, but they are not the determining factor.
On 03.04.2025, Prime Minister of Ukraine Denis Shmygal announced plans to import 4.5 bcm of gas during the gas summer (25 mcm per day) for injection into UGS facilities. Other estimates of import volumes range from 5 to 8 bcm.
Ukraine physically imports gas molecules from Europe through Slovakia (the pipeline's capacity is 42 mcm per day), Hungary (10) and Poland (6.2 until 30.06.2025, 12.4 - from 01.07.2025).
Preparation of physical and commercial infrastructure for the import of natural gas through the Trans-Balkan gas Pipeline in reverse mode was finalised this June. New capacity is 3 mcm per day. This gas pipeline was originally built and has historically been used to supply Russian gas to the Balkans. After the launch of the Turkish stream in 2020, supplies moved from the Trans-Balkan gas pipeline to the Turkish stream due to lower level of hostility towards Russia from transit countries and lower transportation costs. As s consequences The Trans-Balkan gas pipeline went down. Ukraine's refusal to transit Russian gas from 01.01.2025 and relatively independent from Brussels governments of Hungary and Slovakia prompted launch of the Trans-Balkan gas pipeline in the opposite direction. Pipeline is filled by regasified US LNG discharged at new Greek Revithoussa terminal.
Key obstacle to the use this gas pipeline by Ukraine remains higher transportation costs - imports through the terminals of Swinoujscie (Poland) and Krk (Croatia) were cheaper. In Q2 2025, European gas transportation operators made a 46% discount for Ukrainian companies, but this still did not make this route commercially attractive compared to alternatives. Therefore, in the near future, this route will remain a reserve for Ukrainian companies and will be used only if the capacity of cheaper routes through Poland, Hungary and Slovakia are fully utilized.
On 01.07.2025, the operators of the gas transmission systems of Ukraine and Poland (OGTSU and Gaz-Systems, respectively) extended the agreement on guaranteed for Ukraine capacity until 30.09.2026. Moreover guaranteed capacity increased to 12.4 mcm per day (4.5 bcm per year). The Polish route de facto receives regasified LNG from the USA at the Swinoujscie terminal. Polish Orlen is a commercial intermediary, buying LNG from USA on its own account and reselling it to Ukraine (DTEK and Naftogaz).
Brazil
Brazil's LNG regas infrastructure consists of 9 terminals with a total capacity of 36 MTPA. LNG traditionally performs reserving function and insures the country's gas-fired TPPs are well supplied by gas during periods of low domestic hydro generation.
Q2 2025 LNG imports to Brazil amounted to 308 thousand tons. Terminal utilization is a meager 3%.
In early April 2025, Brazil began importing Argentinian pipeline gas. Supply origin is share of French TotalEnergies in gas production at Argentinian Vacas Muertas. Supplies are being transited through Bolivia (with participation of Bolivian state oil and gas company YPBF). Initial volume of supplies is 0.5 mcm per day (equivalent to 2-3 standard LNG shipments per year).
In H2 2025, Brazil's HPP output is expected to decrease, which will increase demand both for electricity imports from Uruguay and Argentina, and for LNG imports.
In Q2 2025 GNA 2 gas-fired TPP (1.7 GW) was commisioned. TPP is located in the area of Porto do Açu LNG regasification terminal. This TPP launch could increase LNG import via this terminal.
All other countries imported less than 2 million tons of LNG in the 2nd quarter of 2024. Detailed import statistics by country are available at the link.
Fleet
Current fleet
As of 01.07.2025, there were 893 operational LNG carriers, including bunkering vessels, FSRU, floating LNG plants and floating storages with 60.0 MT of total cargo hold capacity.
Newbuild
In 2025, LNG carriers with 7.8 MT of total cargo hold capacity are expected to be commissioned. It will be record-breaking volume. Y-o-Y increase is 56%.
South Korea is the leader in LNG shipbuilding. Japan, historic leader in the construction of gas carriers, systematically stopped their construction for internal economic reasons. South Korea has won this competition and currently dominates among existing fleet and among LNG vessel under construction.
China pursue South Korea, moving from building relatively cheap oil tankers and bulk carriers to building much more expensive LNG carriers. China is the number two shipbuilder of LNG carriers right now with a dynamically growing market share. Prospects of Chinese shipbuilding are limitless.
Russia creates its own independent capacities for LNG carriers build up. This is the only remaining option against the background of the refusal of shipyards in South Korea and China to build gas carriers for Novatek. The key asset is the Shipbuilding Complex Zvezda in Primorsky krai. The task is complicated by the fact that you need to build not only a LNG carrier itself, but also domestically produce all vessel and LNG equipment components. No country has yet solved this problem.
Secondary market
Observed secondary market of LNG carriers in Q2 (April - May data as of now) was limited to one transaction. A LNG carrier (2006, 79 kt DWT) was sold for 2.3 bRUB / 103 mAED / 2.4 bINR / 202 mCNY / 28 mUSD.
Demolition
There weren’t records in the second quarter on a LNG carrier demolition. There were three such cases in the first quarter.
Freight rates
In the second quarter, freight rates for LNG carriers recovered after falling in the first quarter. As of 04.07.2025, the freight rate was 23 kUSD per day for a standard tri-fuel (TFDE) LNG carrier with capacity of 73 ktons of LNG in the Pacific and Indian oceans. Rates are doubled Q-o-Q.
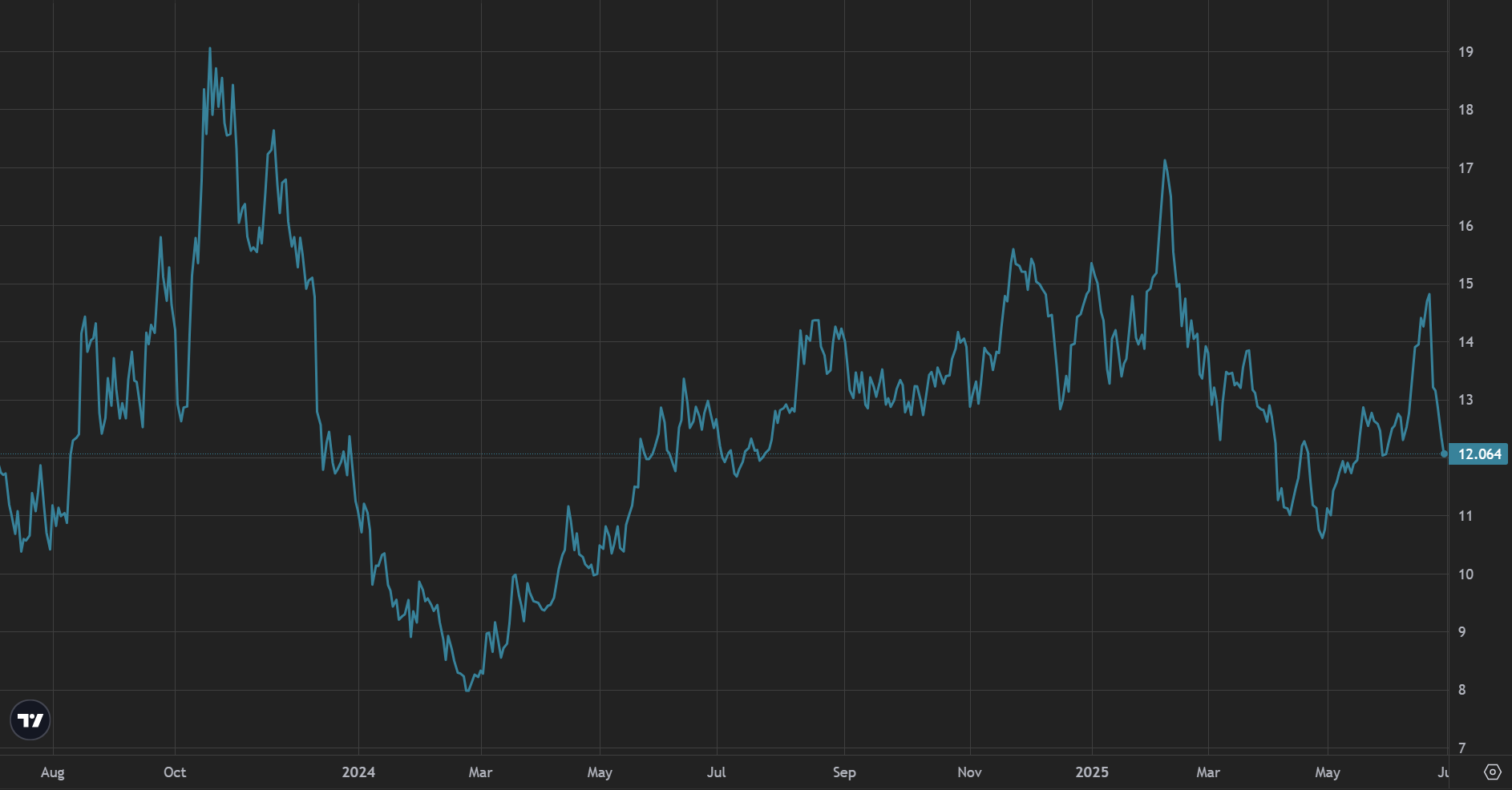
Spot freight rate of an TFDE LNG carrier with 73 kt capacity in Pacific and Indian Ocean region in July 2023 - June 2025, USD /day
Operating expenses for the maintenance of gas carriers can be estimated at 1.2 mRUB / 52.8 kAED / 103 kCNY/ 1.2 mINR /14.4 kUSD per day for a new gas carrier - 1.5 mRUB / 63 kAED / 123 kCNY /1.5 mINR / 17.2 kUSD for a 20-year-old gas carrier with a standard load capacity of 150-170 thousand cubic meters. Thus, after a loss-making first quarter, the owners of LNG gas carriers returned to operating profit in the second quarter of this year.
However, over the long-term horizon, owning a fleet of gas carriers is increasingly becoming more useful for LNG plant owners to operationally control its export than for independent shipping companies to make a profit.
US attack on Chinese shuipbuiding industry
One of the first attacks of the second Trump administration was aimed at curbing Chinese shipbuilding industry and simultaneous support of almost extinct US shipbuilding. This pressure could cause huge problems for Chinese economy with high multiplication effect on the whole Chinese economy. At the same time, it is unlikely that the US shipbuilders will win anything in this battle. South Korea will be clearly beneficiary and will raise the price tag for its new LNG carriers.
In the first quarter, the United States imposed an additional duty for the port entry of LNG carriers built in China and/or flying the Chinese flag. In April application of this duty has been revised regarding LNG carriers and some other vessels. Key change relevant of LNG industry that application of additional port duty for China-related LNG carriers postponed to 14.10.2028.
Potential amount of postponed till 2028 duty is estimated as follows: 140 USD (2028 amount) per net ton of LNG carrier, build in China . Capped at 5 portcall per year for each vessel. It is equivalent 375 mRUB / 17.5 mAED / 34.1 mCNY / 409 mINR /4.8 USD per portcall for standard 73kt LNG carrier.
Starting 2028 this amount will be applicable both to Chinese-owned or operated carriers, and other as well. Presumably there will be some exemptions for US-flagged or owned by US company LNG carriers, which were built in China. In addition it is announces that companies could recieve duty refund in case they will order a US-built LNG carrier. But it does not exist.
In addition starting 17.04.2029, the share of US LNG exports required to be transported on US-built, US-flagged, and US-operated vessels will gradually increase each year, from 1% in the first two years to 15% by April 2047. These restrictions will increase incrementally over 22 years.
5% of the current fleet of LNG carriers was built in China. 25% of LNG carriers under constrution are being built in China.
As of 01.07.2025, 42 gas carriers are flying the Chinese flags, including 35 gas carriers flying Hong Kong flag.
The consequences for the LNG market depend on the overall outcome of the US-Russia and US-China confrontations and effectiveness of Russia-China cooperation. It is difficult to predict these consequences, but we will try to do it a form of extreme scenarios:
The scenario of “Splitting the LNG trade into parts“. In this scenario, China, losing the US market for direct supply of its products of a wide range, integrates more with friendly and neutral countries for it (CIS, Africa, Latin America). In terms of LNG, this means China abandoning LNG supplies from the United States and refocusing on LNG supplies from Russia while maximizing pipeline gas flows from Central Asia and Myanmar. In this case, Russian gas companies find both a sales market and solve all problems with the payment and maintenance of the fleet of gas carriers. USA will is increase LNG supplies to EU, UK, Japan and South Korea.
The “US victory in the trade war" scenario. In this scenario, China increases LNG imports from the United States, similar to the results of Trump's first trade war against China. Imports of LNG from Russia are likely to decrease, as well as the provision of technical services and equipment supplies by Chinese companies to Russian contractors in the LNG industry. The LNG market remains unified, but without Russia's participation in it.
LNG bunkering
Singapore, Rotterdam and starting this year Shanghai are the leading LNG bunkering centers in the world.
In Singapore, sales of LNG as bunker fuel in April - May 2025 amounted to 87 kt (38 kt per month 2025 YTD). In April 2025, the Maritime and Port Authority of Singapore announced plans to increase the volume of LNG bunker sales to 3 million tons in 2028 (250 kt per month). Thus, a sixfold increase in volumes is planned compared to 460 kt in 2024. Issuing new licenses for LNG bunkering and the construction of the second LNG terminal in Singapore are underway to achieve this goal.
Learn more about Singapore's LNG industry here.
In Rotterdam, 96 kt LNG were sold as bunker fuel in Q1 (32 kt per month).
In Shanghai, bunkering volumes in January-May 2025 increased by 61% YoY and amounted to 144 kt (29 kt per month). Over 200 bunkering operations were carried out in 5 months (80 for the whole of last year). Shanghai International Port Group has ordered construction of another bunkering vessel, which will begin operations in the first half of 2027. This will double the volume of LNG bunkering operations at the port.
Huaihe Nengyuan Qihang LNG bunker vessel
Also, significant volumes of LNG bunker are sold in Barcelona (Spain), St. Petersburg (Russia), Zeebrugge (Belgium), Tananger (Norway), Klaipeda (Lithuania), Inku (Finland), Long Beach (USA), in other US ports, in ports of South Korea and Japan.
Map of the location of 43 operating LNG bunkers as of 07.07.2025
Price dynamics
Asia
The spot price for the supply of LNG to East Asia (JKM) on 07.07.2025 was 12.35 USD/ MMBtu, which is equivalent to 36.33 RUB / 1.69 AED / 3.30 CNY / 39.55 INR / 46.1 US cents per cubic meter of methane.
Price quotes for spot shipments of LNG to ports in Japan, South Korea and Taiwan Province of China (JKM) in July 2023 - June 2025, USD / MMBtu
Wholesale prices remained flat compared to the end of Q1, although have volatiled a lot. The key reason behind market jumps is Trump's foreign policy - from a geopolitical discount in April-May (Trump's “reciprocal“ tariffs) to a temporary geopolitical premium in June (the US attack on Iran and the expectation of retaliation). Insiders probably made a lot of money on stock trading in the second quarter.
Wholesale LNG prices at a port of an importing country (DES) do not include the costs of regasification, distribution to end users, other taxes, fees and profits of gas companies. Energy in Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan continues to be very expensive.
Mid-term futures quotes generally remained at the same level compared to end of Q1.
Long-term LNG futures prices on the Singapore Stock Exchange suggest a decline in the price of LNG starting in the summer of 2028. During the first quarter, long-term futures for 2026 and 2027 declined, which may indicate expectations for an acceleration in the decline. Current long-term futures quotes as of 04.07.2025:
2026 - 12.30 dollars per million British thermal units (quote on 08.01.2025 - 12.55, on 08.04.2025 - 11.95).
2027 - 11.32 dollars per million British thermal units (quote on 08.01.2025 - 10.45, on 08.04.2025 - 10.28). A decrease of 8% from the current spot price.
2028 - 10.18 dollars per million British thermal units (quote on 08.01.2025 - 9.00, on 08.04.2025 - 9.23). A decrease of 18% from the current spot price.
Despite the fact that trading in these long-term futures is not very liquid, it reflects the market's opinion about the LNG surplus during these time periods. The slope of the futures curve decreased in the second quarter. Thus, the gas surplus period shifted to the right.
EU
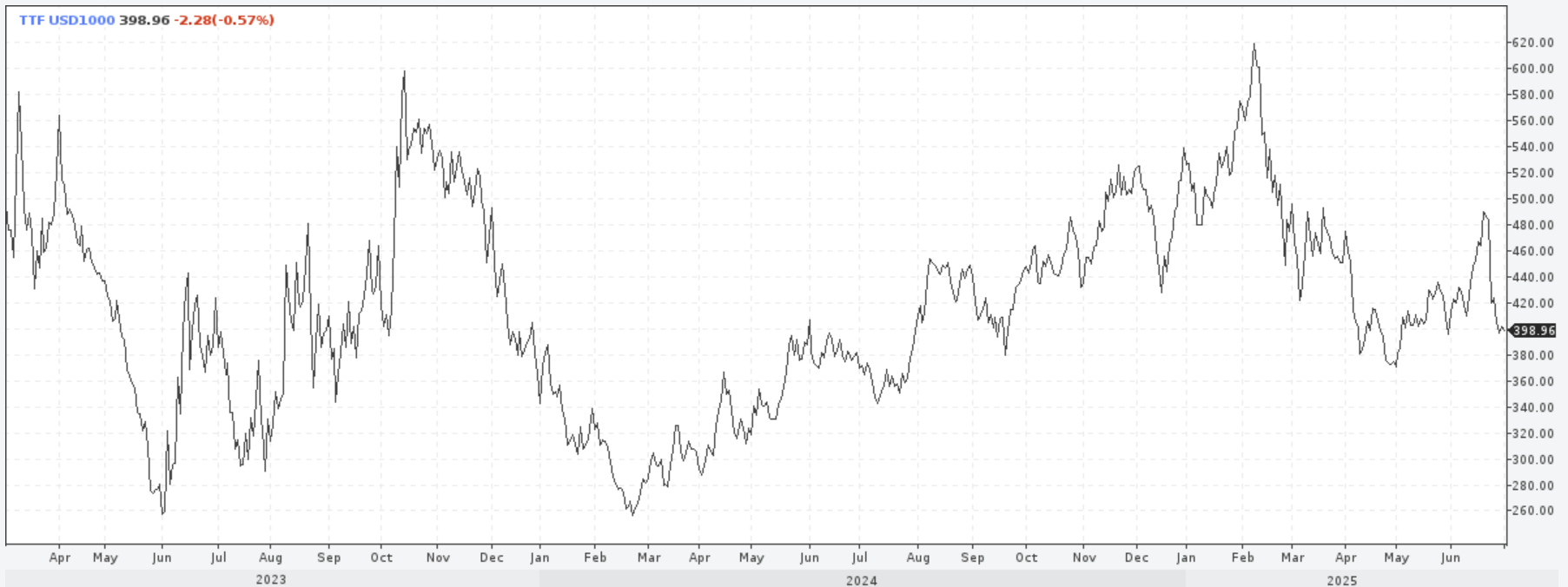
Spot gas price in the EU (TTF) as of 01.07.2025 was 405 USD per thousand cubic meters, which is equivalent to 31.93 RUB / 1.49 AED / 2.90 CNY / 34.76 INR / 40.5 US cents per cubic meter of natural gas. The decrease from the peak reached in mid-February, at 620 USD per thousand cubic meters, was 35%. However, prices continue to be above the level of Q2 2024.
Exchange prices for gas at the TTF hub (Netherlands) in 2023-2025, dollars per thousand cubic meters
European gas prices continue to be high. Voluntary self-ban of import of cheap Russian piped gas to EU leads to transfer of energy-intensive industries, primarily chemical ones, from Europe to the United States and the Middle East, as well as increased global competition from Chinese manufacturers, who continue to massively introduce gas processing facilities.
Russia
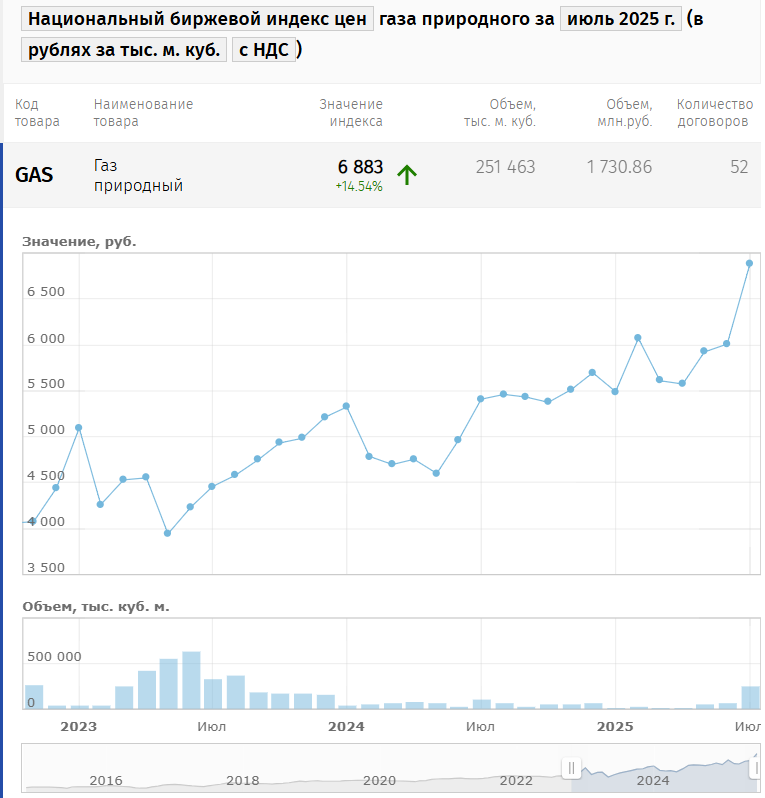
Settlement of the National exchange index of natural gas for July 2025 delivery on the Petersburg Exchange (formerly the St. Petersburg International Mercantile Exchange, SPIMEX) was 5.7 RUB / 0.27 AED / 0.52 CNY / 6.16 INR / 5.7 US cents per cubic meter of natural gas (6.88 RUR / 0.32 AED / 0.63 CNY / 7.45 INR / 8.8 US cents per cubic meter, including VAT). QoQ growth - 22% despite moving from winter prices to summer prices.
National exchange index of natural gas for July 2025 delivery, RUB / thousand cubic meters including VAT
Q2 exchange traded volumed amounted to 3.4 bcm, QoQ decreased compared to 4.2 bcm in Q1. The volume natural gas traded on the exchange, including secondary sales, is 2.9% of domestic consumption of natural gas.
Regulated domestic residential prices increased on 01.07.2025. 2025 H2 weighted average price will be 8.32 RUB / 0.39 AED / 0.76 CNY / 8.99 INR / 10.6 US cents per cubic. The growth in rubble equivalent is 10.3%. The growth of industry and power generation domestic gas prices is 21.3%. It equalizes residential and industry prices. Earlier, in 2023-2024, a less significant growth was planned for 2025 price renewal - only 8%. Thus, this price increase was higher tha originally planned. It is worth noting that the inflation target set by Central Bank of Russian is 4%. The key rate as of 07.07.2025 is 20%. Higher gas prices will delay achievement of the inflation target.
USA
Wholesale gas prices in the United States continue to be among the lowest in the world. August 2025 Henry Hab price as of 04.07.2025 was 3.4 USD/mmBTU, which is equivalent to 9.54 RUR / 0.44 AED / 0.87 CNY / 10.38 INR / 12.1 US cents per cubic meter of natural gas. QoQ decrease - minus 22%.
Taking into account the pace of commissioning of LNG projects on Mexican Gulf coast and the political pressure of the United States on its competitors in this market, pricing in the LNG market is switching to the following formula: <wholesale price of gas in the United States> + <payment for transportation and supply of gas to the LNG plant> + <fee for gas liquefaction> + <freight to the consumer>. As of 30.06.2025, this half of the LNG price in East Asia can be estimated at 8.5 USD/MMBTU. It is this formula price that will be the asymptote for futures prices.
Market view for Q3 2025
In the third quarter, primary consumption of natural gas in traditional LNG markets will increase compared to the traditionally low second quarter. A key growth factor is the increase in air conditioning the Middle East, South and Southeast Asia, and Europe. The focus of market uncertainty is on poor countries of the region - Egypt, Iraq, Pakistan, Bangladesh (with a combined population of 560 million people).
Replenishment of EU UGS storages is on track. It will maintain relatively high LNG, but no negative surprises are expected here.
Trump could add a new shock to the LNG market any time. It includes new initiatives on so-called “reciprocal” tariffs (it is happening right now), new wars (against Iran or some other countries), and the beginning of a new round of pressure on Russia, China and Iran.
Spot DES LNG price is expected to remained in Q3 in current 12-13.5 MMBtu.
LNG spot freight prices, after stabilization in the second quarter, are expected to be relatively stable in the third quarter. Daily charter rate for 73 kt TFDE LNG carrier in Pacific region is expected to be in 19-23 kUSD/day range.
Notes:
Join Seala AI Linkedin page to be informed for all new future releases with new dashboards and insights.
News are available in Seala AI telegram channel.
Full set of reports for each country and much more information are available via Seala AI terminal.